Leukemia
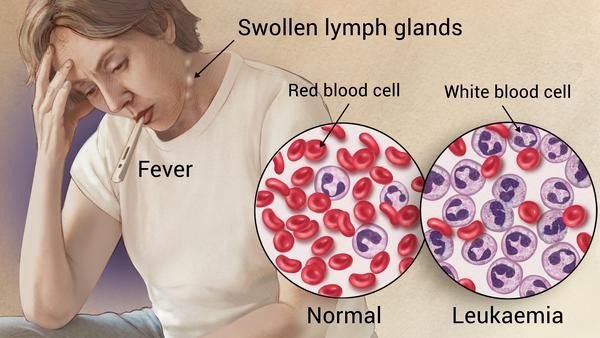
Leukemia is also a blood cancer caused by a rise in the number of white blood cells in your body. Those white blood cells crowd out the red blood cells and platelets that your body needs to be healthy too. The extra white blood cells don’t work right.
Different types of leukemia can cause different problems. You might not notice any signs in the early stages of some forms. When you do have symptoms, they may include;
No one knows exactly what causes leukemia. People who have it have certain unusual chromosomes, but the chromosomes don’t cause leukemia. You can’t prevent leukemia, but certain things may trigger it. You might have a higher risk if you;
How does leukemia happen?
Blood has three types of cells: white blood cells that fight infection, red blood cells that carry oxygen, and platelets that help blood clot. Every day, your bone marrow makes billions of new blood cells, and most of them are red cells. When you have leukemia, your body makes more white cells than it needs. These leukemia
cells can’t fight infection the way normal white blood cells do. And because there are so many of them, they start to affect the way your organs work. Over time, you may not have enough red blood cells to supply oxygen, enough platelets to clot your blood, or enough normal white blood cells to fight infection.
Classifications
Leukemia is grouped by how fast it develops and gets worse, and by which type of blood cell is involved. The first group, how fast it develops, is divided into acute and chronic leukemia.
Types of leukemia
The four main types of leukemia are;
Diagnosis
Your doctor will need to check for signs of leukemia in your blood or bone marrow. They might do tests including;
Treatments
The treatment you get depends on the type of leukemia you have, how far it’s spread, and how healthy you are. The main options are;
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells in your blood and bone marrow. You can get the medicine;
Radiation uses high-energy X-rays to kill leukemia cells or keep them from growing. You can get it all over or in only one part of your body where there are a lot of cancer cells. Biologic therapy, also called immunotherapy, helps your immune system find and attack cancer cells. Drugs like interleukins
and interferon can help boost your body's natural defenses against leukemia. Targeted therapy uses drugs to block specific genes or proteins that cancer cells need to grow. This treatment can stop the signals that leukemia cells use to grow and divide, cut off their blood supply, or kill them directly. A stem cell
transplant replaces the leukemia cells in your bone marrow with new ones that make blood. Your doctor can get the new stem cells from your own body or from a donor. First, you'll have high doses of chemotherapy to destroy the cancer cells in your bone marrow. Then, you'll get the new stem cells through an infusion into one of your veins. They will grow into new, healthy blood cells.
Surgery
Your doctor can remove your spleen if it’s filled with cancer cells and is pressing on nearby organs. This procedure is called a splenectomy.
Symptoms
Causes and Risk Factors